Monday, November 4, 2013
Asexual Reproduction of Fungi
It is estimated that as many as 20,000 species of fungi reproduce asexually, among them Molds and Yeasts.
Molds reproduce rapidly and produce haploid spores. Many of their species form visible mycelias. Their hyphae is tubular and have identical nuclei, therefore they are considered a single colonial organism.
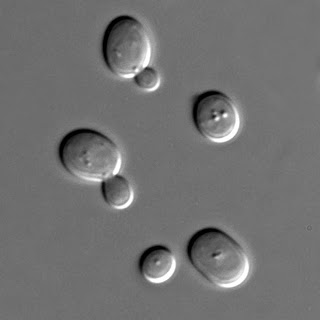
Yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis or budding. When it reaches maturity, it separates and begins its own life. The budded organism is a clone, or a genetically identical offspring of the parent organism.
A large group of fungi called the Deuteromycota also known as conidial fungi, or fungi that reproduce through vegetative spores, they lack a known sexual stage in their life cycle. If a sexual stage is discovered, that species will be reclassified based on its type of sexual structures.
Vocabulary
Deuteromycetes. The Fungi imperfecti, or Deuteromycota, are fungi which do not fit the established taxonomic classifications of fungi based on biological species concepts, morphological characteristics o sexual structures, because their sexual form of reproduction has never been observed.
Mold. A natural substance in the form of a woolly or furry growth of tiny fungi that appears when organic material lies for a long time exposed to air.
Yeast. A microscopic fungus consisting of single oval cells that reproduce by budding, and are capable of converting sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)

No comments:
Post a Comment